Image recognition vs. pattern recognition – all the same?
Checking industrial goods for quality? With machine vision, nothing could be easier! However, there is no such thing as one machine vision solution. The differences between the individual options in terms of recognition capability, capabilities and precision are great. In addition to sensor selection, this is also due to the quality inspection algorithms used. Currently, the two most commonly used are pattern recognition and image recognition. But what exactly differentiates these two methods?
Both are different variants of machine vision in computer science. That is, image and pattern recognition conceal two approaches and thus two differently structured types of algorithms. What they have in common is that they structure image content using certain procedures and break down its complexity in such a way that image and pattern recognition become manageable for the algorithms. Only then does the code search for specific properties in this data – either certain patterns or predefined objects and people.
But that’s where the similarities end. Because while pattern recognition still performs relatively straightforward operations, image recognition goes deeper.
Basic operator in image processing: pattern recognition
Pattern recognition means finding correlations between individual images and/or objects and labeling them correctly. It is therefore particularly suitable for simple inspection and testing tasks. The strengths of pattern recognition include, in particular, finding, tracking and smoothing contours. This makes it particularly suitable for inspecting sharp edges, but also for performing a completeness check (e.g., can a seal be identified as a circle?).
A frequently used algorithm in pattern recognition is the normalized gray value correlation. The method works with light changes from light to dark and identifies edges in this way. For the algorithm to work reliably, it depends on a constant scenario: The captured objects must always have the same size and orientation. Although the latest developments can compensate for tolerances to a limited extent, there is no question of flexibility here.
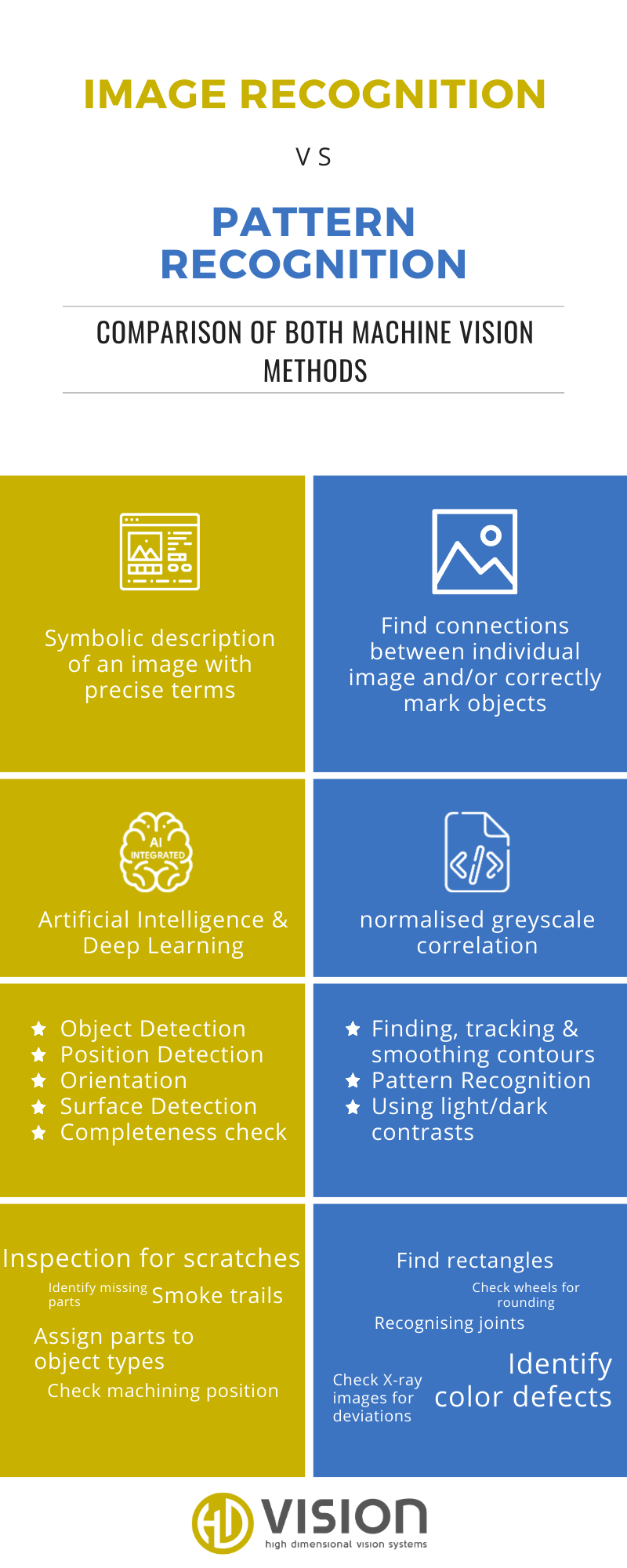
Image recognition: Artificial intelligence for more demanding tasks
Image recognition, on the other hand, concerns the symbolic description of an image with concrete terms such as “dog,” “house,” etc. The process explicitly does not search for the same size or orientation. The process explicitly does not look for patterns or commonalities in other images. Instead, image recognition works with the help of artificial intelligence and deep learning. The neural networks used in this process are so numerous and so strongly interconnected that it is not possible to trace them back to their origin.
In order for these connections to come to the right conclusions, it is necessary to train the image recognition for each task. Only then can it reliably recognize objects. In return, it can do this even under more demanding conditions and from changing angles. Shadows, lighting effects and patterned image backgrounds are also no longer KO criteria.
Because of this, image processing is able to recognize objects, their position and location. This can be used, for example, to
- automatically label images in image databases,
- recognize images and sections and assign them to a product,
- identify faces,
- detect deviations from the standard
- detect registration marks so that accurate placement can be achieved in the industry
- inspect surfaces, and more.
Image vs. pattern recognition: does AI trump all?
Image recognition offers image processing more advanced recognition options than pure pattern recognition. Still, this should not be dismissed as an outdated technology. Often, pattern recognition is already sufficient for the actual purpose. This simpler application is also accompanied by a lower development effort: no training of neural networks is necessary here. For complex tasks, however, it is better to stick to image recognition. Two methods, two application areas: Image and pattern recognition thus complement each other ideally.
Integrated 3D object detection for the handling of complex workpieces



